Host/Falco Runtime Security
Falco is an open-source runtime security monitoring tool designed to detect anomalous activity and security breaches in containerized environments, with a strong focus on Linux systems. It's particularly useful for environments that rely on Kubernetes, Docker, and other container runtimes. The tool functions by observing system calls and leveraging kernel-level introspection, which allows it to monitor a variety of security events such as privilege escalation, unauthorized access, or suspicious file system activity.
Key Features and Technical Aspects
-
Kernel-Level Monitoring
Syscall Interception: Falco monitors system calls (syscalls) to detect suspicious activities. It works by attaching to the kernel's syscall interface, allowing it to observe the execution of low-level operations across the entire system. This includes file access, network connections, process creation, and more.
eBPF (Extended Berkeley Packet Filter): Starting from version 0.26, Falco uses eBPF for efficient and low-latency monitoring. eBPF allows Falco to dynamically load kernel modules to trace system calls and other kernel activities with minimal overhead, without requiring kernel modifications.
-
Event Rules and Customization
Rule Engine: Falco operates by analyzing system call events against predefined security rules. These rules define what constitutes suspicious or malicious behavior (e.g., attempts to open sensitive files, privilege escalation attempts, network connections to suspicious ports). Rules can be customized to detect environment-specific threats.
YAML-Based Rule Syntax: Falco's rule syntax is written in YAML, making it user-friendly while offering flexibility for complex matching conditions. Users can specify conditions for specific syscalls, the identities of users or processes involved, and the type of behavior expected (e.g., read/write operations on specific directories).
-
Event Flow and Detection Mechanism
Event Collection: Events are captured by Falcon through system calls using a kernel module or eBPF programs, which capture detailed metadata about the process, user, and system resources involved in the event.
Filtering: Events are processed in real time by filtering through Falco’s rule set. Each event is matched against a defined set of rules to determine if it is suspicious or malicious.
Alert Generation: When a suspicious or malicious event is detected, Falco triggers an alert, which includes details about the event such as the involved process, user, syscall, and the rule that was violated. Alerts can be sent to multiple outputs, including Slack, syslog, or any other configured alerting system.
-
Container Runtime Support
Container Visibility: In containerized environments, Falco can track the behavior of individual containers and correlate container-level activities to host-level system calls. It identifies if a container performs any potentially dangerous actions, such as accessing sensitive files outside its designated filesystem or attempting to open privileged network ports.
Kubernetes Integration: For Kubernetes, Falco integrates with Kubernetes Audit logs to correlate activities between containers and the host system. This provides visibility into whether containers are adhering to security policies and limits.
-
Output and Actionable Alerts
Flexible Alerting: Once an event is detected, Falco can generate alerts in several formats, including JSON, plain text, and structured logging formats, which can be integrated with SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) systems for further analysis and correlation.
Custom Actions: Alerts can trigger specific actions such as executing a custom script, calling a web service, or sending data to monitoring dashboards and facilitating automated responses to detected security events.
-
Integration with Other Security Tools
SIEM Integration: Falco supports integration with SIEM solutions, such as Splunk, ELK Stack, and other log aggregation platforms, which allows centralized logging and deeper analysis of security incidents.
Security Information Sharing: By sending alerts to external systems (like Prometheus or Slack), Falco makes it easier for security teams to monitor the system in real time and collaborate on incident response.
Falco provides a robust and efficient runtime security solution for Linux systems and containerized environments by leveraging kernel-level monitoring and real-time event analysis. Its flexible and extensible rule engine, combined with integration with existing security frameworks (such as SELinux and Kubernetes), makes it a powerful tool for detecting malicious activity and securing cloud-native applications and infrastructures. By focusing on low-level system calls, syscall metadata, and custom detection rules, Falco allows for effective monitoring with minimal performance impact.
Falco is primarily a visibility engine. It automatically selects a set of syscalls to trace using the union between a base set of syscalls needed for its internal state management (eg, open, close, clone) and the minimum set of syscalls required by the ruleset (adaptive syscall selection). Falco rules express conditions on syscall events or plugin-generated data. While effective for many use cases, syscall-based monitoring can be susceptible to TOCTOU (time-of-check/time-of-use) vulnerabilities where certain operations can occur between the syscall check and the actual kernel action, creating opportunities to evade monitoring.
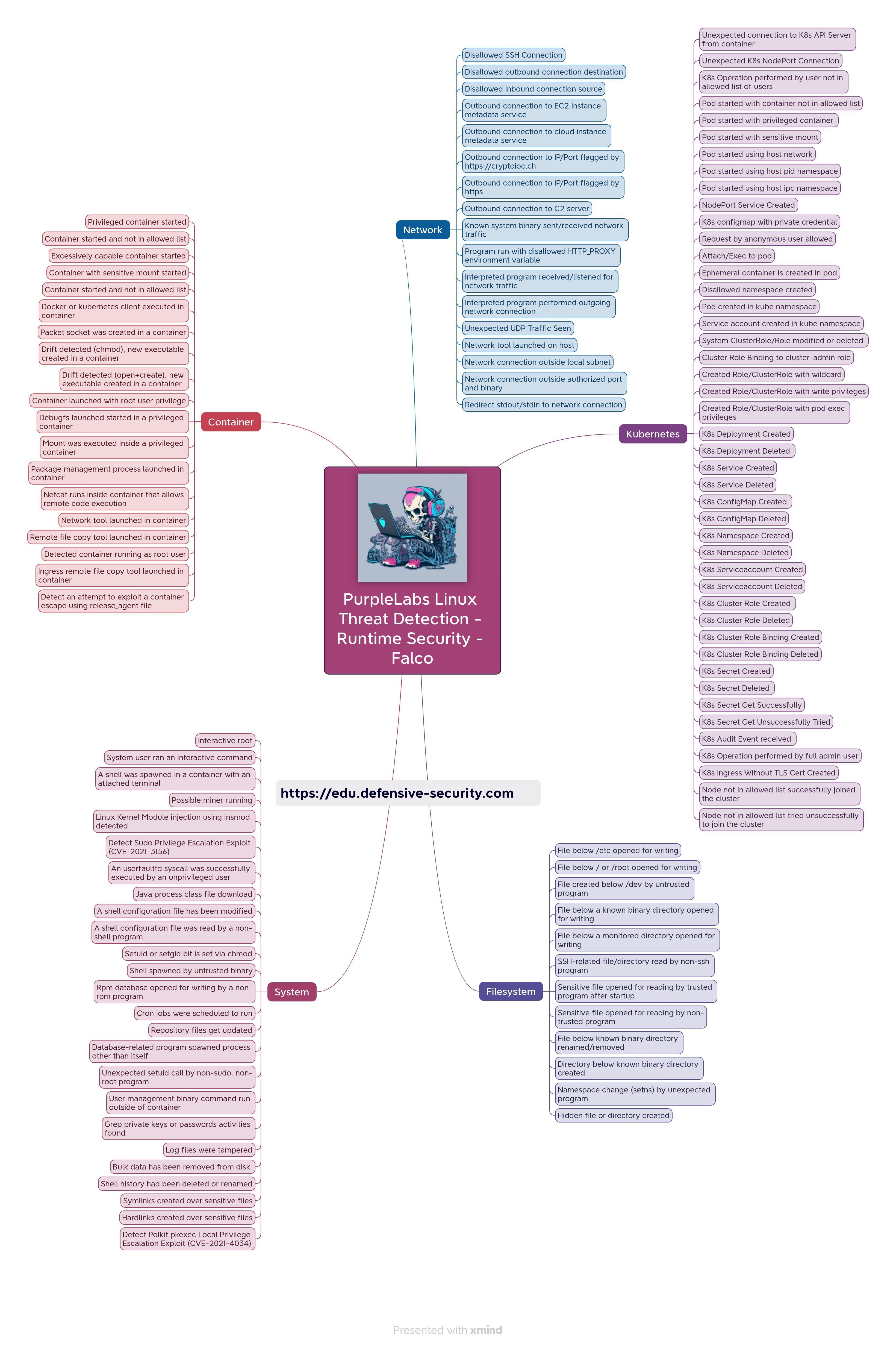
The list of supported, contextual host-oriented Falco detection rules is here:
Clear Log Activities
Create Hardlink Over Sensitive Files
Create Symlink Over Sensitive Files
Debugfs Launched in Privileged Container
Detect release_agent File Container Escapes
Directory traversal monitored file read
Disallowed SSH Connection Non-Standard Port
Drop and execute new binary in container
Execution from /dev/shm
Fileless execution via memfd_create
Find AWS Credentials
Linux Kernel Module Injection Detected
Netcat Remote Code Execution in Container
PTRACE anti-debug attempt
PTRACE attached to process
Packet socket created in container
Read sensitive file trusted after startup
Read sensitive file untrusted
Redirect STDOUT/STDIN to Network Connection in Container
Remove Bulk Data from Disk
Run shell untrusted
Search Private Keys or Passwords
System user interactive
Terminal shell in container
Adding ssh keys to authorized_keys
BPF Program Not Profiled
Backdoored library loaded into SSHD (CVE-2024-3094)
Change namespace privileges via unshare
Change thread namespace
Contact EC2 Instance Metadata Service From Container
Contact cloud metadata service from container
Create files below dev
DB program spawned process
Delete or rename shell history
Launch Excessively Capable Container
Launch Ingress Remote File Copy Tools in Container
Launch Package Management Process in Container
Launch Privileged Container
Launch Remote File Copy Tools in Container
Launch Suspicious Network Tool in Container
Launch Suspicious Network Tool on Host
Modify Shell Configuration File
Mount Launched in Privileged Container
Network Connection outside Local Subnet
Non sudo setuid
Potential Local Privilege Escalation via Environment Variables Misuse
Program run with disallowed http proxy env
Read environment variable from /proc files
Read ssh information
Schedule Cron Jobs
Set Setuid or Setgid bit
System procs network activity
Unexpected UDP Traffic
User mgmt binaries
Basic Interactive Reconnaissance
Container Drift Detected (chmod)
Container Drift Detected (open+create)
Container Run as Root User
Create Hidden Files or Directories
Decoding Payload in Container
Detect crypto miners using the Stratum protocol
Detect outbound connections to common miner pool ports
Interpreted procs inbound network activity
Interpreted procs outbound network activity
Java Process Class File Download
Launch Disallowed Container
Launch Sensitive Mount Container
Mkdir binary dirs
Modify Container Entrypoint
Modify binary dirs
Netcat/Socat Remote Code Execution on Host
Polkit Local Privilege Escalation Vulnerability (CVE-2021-4034)
Read Shell Configuration File
Sudo Potential Privilege Escalation
Unexpected inbound connection source
Unprivileged Delegation of Page Faults Handling to a Userspace Process
Update Package Repository
Write below binary dir
Write below etc
Write below monitored dir
Write below root
Write below rpm database
Outbound Connection to C2 Servers
Unexpected outbound connection destination
-
Disallowed SSH Connection
You can access the full list of default rules and associated lists/macros via the Falco Rules Explorer:
INSTALL & ENABLE FALCO:
@ TARGET_X:
# edrmetry-engine-mgmt.sh install_falco
# edrmetry-engine-mgmt.sh enable_falco
# edrmetry-engine-mgmt.sh status | grep -i falco
[**YES**] HOST Falco Runtime Security is running.
# ps uax | grep falco
root 680 0.7 2.7 319360 157124 ? Rsl Oct28 94:08 /usr/bin/falco -o engine.kind=modern_ebpf
root 681 0.0 0.6 5527676 35444 ? Ssl Oct28 0:38 /usr/bin/falcoctl artifact follow --allowed-types=rulesfile
root 393470 0.0 0.0 6408 2208 pts/1 S+ 17:53 0:00 grep --color=auto falco
# systemctl status falco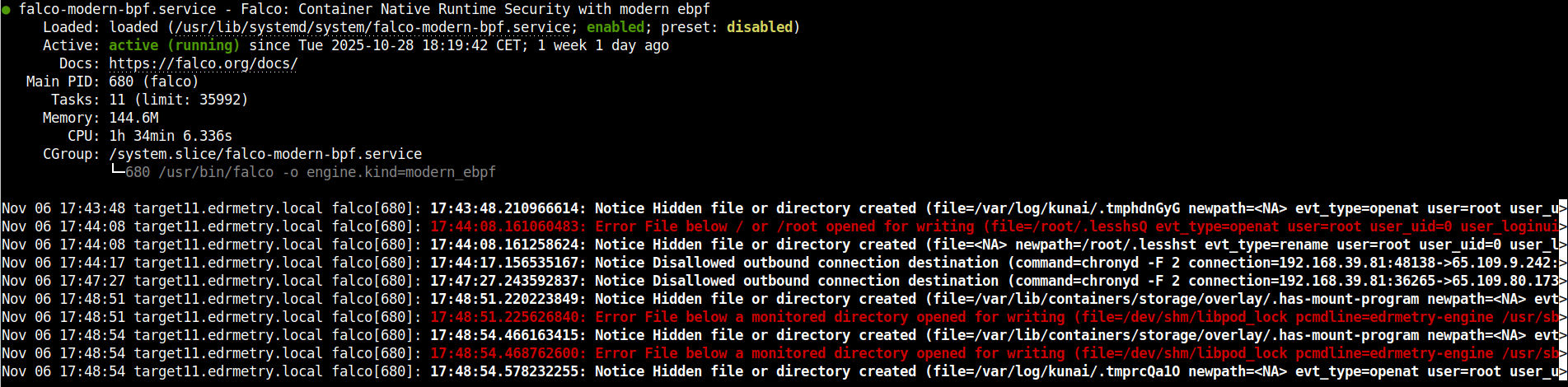
FALCO CONFIGURATION:
@ TARGET_X:
# ls -al /etc/falco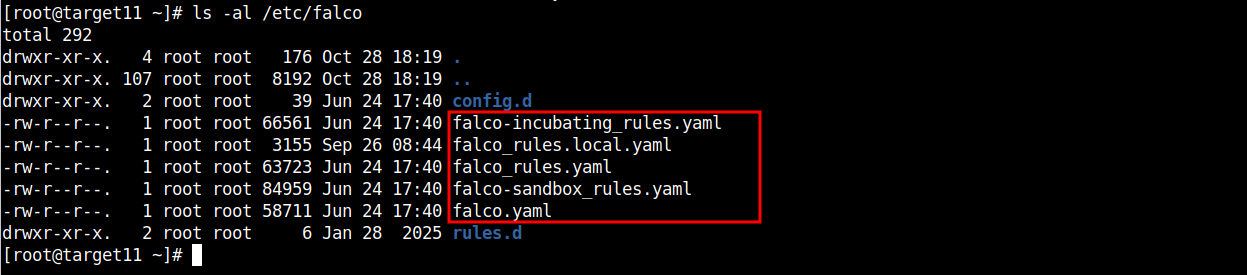
FALCO EVENTS:
Splunk Falco Events:
index=unix falco host="targetX.edrmetry.local"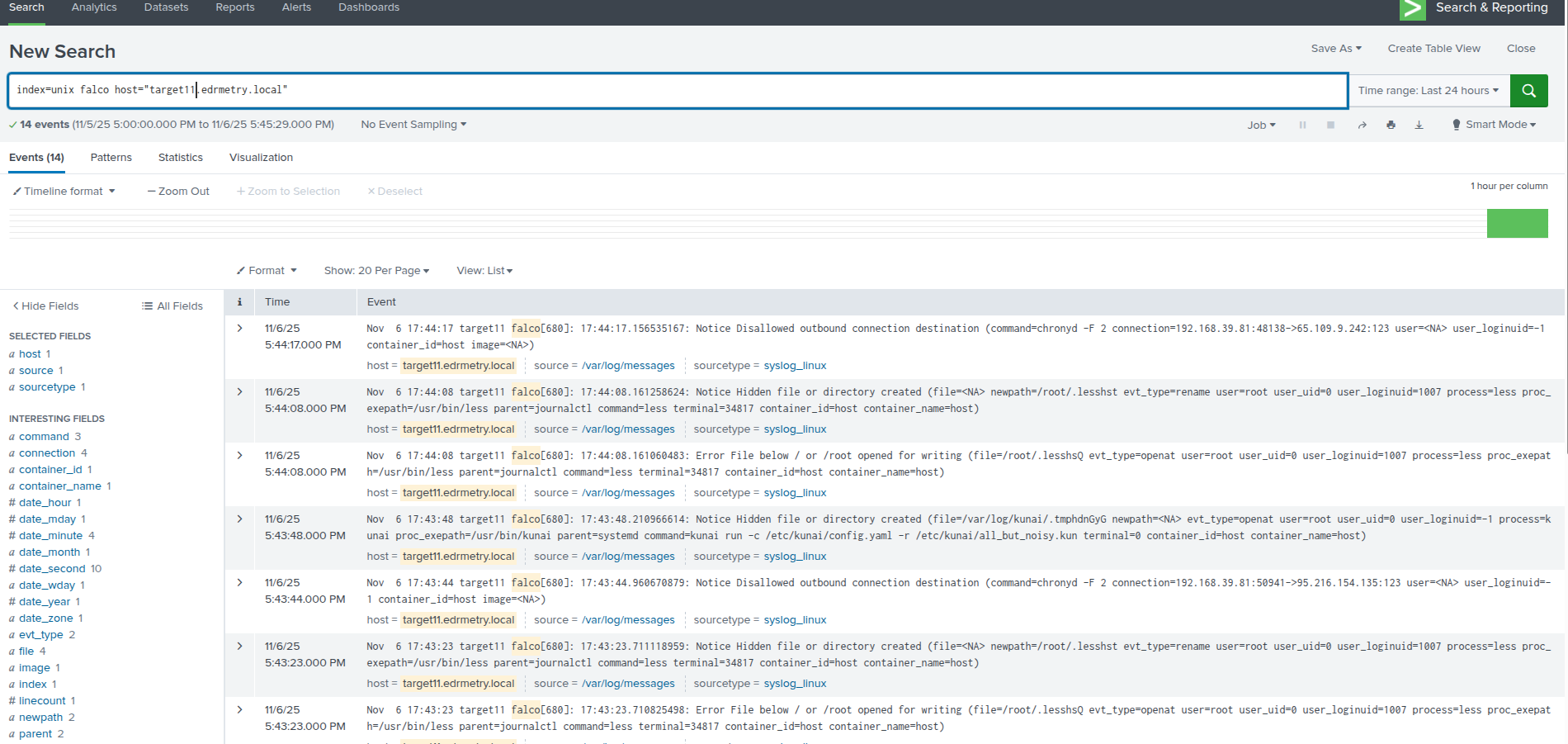
CLI Syslog Falco events:
# tail /var/log/messages -n1000 | grep falco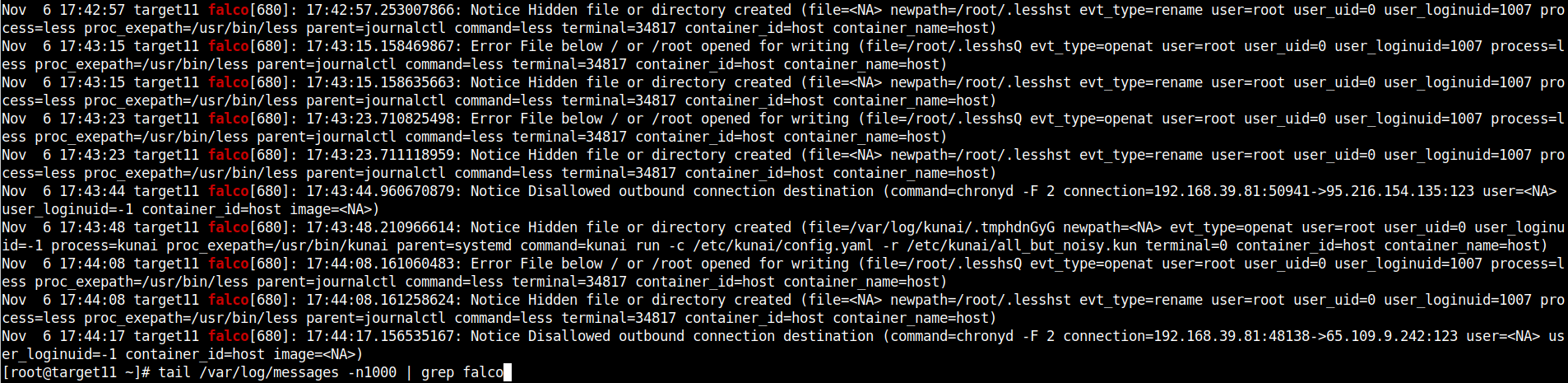
CLI journalctl Falco events:
# journalctl -f -u falco-modern-bpf.service -S today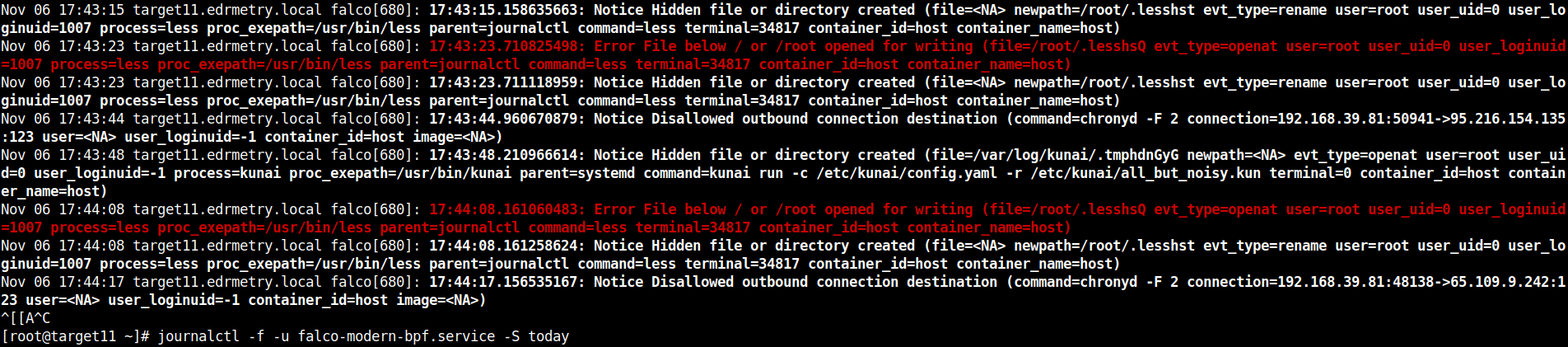
LINKS:
-
Migrating from Falco to Tetragon: A Guide for Transitioning Your Runtime Security Stack:
-
Falco Rules Explorer:
-
Falco - Evasion Techniques:
-
DEF CON 30 - Rex Guo, Junyuan Zeng - Trace me if you can: Bypassing Linux Syscall Tracing:
-
Adaptive Syscalls Selection in Falco: