Learn Linux Attack, Detection, and Live Forensics based on hands-on analyses of user space and kernel space Linux rootkits, C2 frameworks, and tools. Create low-level Linux attack paths, know better Linux internals, improve your Linux detection, understand the need for Linux telemetry, and stay prepared for Linux threats.
This package includes MATERIALS ONLY for an unlimited time. You can purchase the PurpleLABS VPN Access package separately.
Since version v2.0 was published on 10/01/2026, access to v1.0 MATERIALS will be provided by default when purchasing v2.0. Check out Linux Attack, Detection and Forensics v2.0 - Hands-on Purple Teaming Playbook
Use PurpleLABS as a Cyber Range advanced R&D environment for your own red/blue security research needs or as a part of the course, where you will study hands-on labs that we have carefully prepared. You can purchase separately a 90-day VPN PurpleLabs access:
You can find the extended recommendation list here: https://edu.defensive-security.com/about
"I had the pleasure of completing Leszek’s exceptional course on Linux Attack and Live Forensics At Scale. I am especially impressed by the depth of each topic and Leszek's ability to simplify intricate concepts, making it an invaluable learning experience for even seasoned professionals. The hands-on approach, particularly in experimenting with the latest offensive techniques from stealthy rootkits to C2 frameworks and so much more, using relevant open-source tools for detection, significantly enhances the value for any security professional. Leszek's continuous incorporation of new topics further enriches the course's value, complemented by exceptional support. Undoubtedly, it has elevated my skills in purple teaming / learning new offensive and defensive techniques and I highly recommend Leszek’s course to anyone looking to enhance their skills in this area."
Senior Security Engineer @ Google
"I've been having fun doing the Defensive Security Linux Attack and Live Forensics course."
Attackers constantly find new ways to attack and infect Linux boxes using more and more sophisticated techniques and tools. As defenders, we need to stay up to date with adversaries, understand their TTPs and be able to respond quickly. The combination of low-level network and endpoint visibility is crucial to achieving that goal. For DFIR needs
we could go even further with proactive forensics inspections. This training will guide you through different attack-detection-inspection-response use cases and teach critical aspects of how to handle Linux incidents properly.
This course helps create and understand low-level Linux attack paths, improve your Linux detection coverage, see in action many Open Source DFIR/defensive projects, and understand the need for Linux telemetry, especially including Kubernetes clusters where Runtime Security solutions are a must these days. The techniques and attack paths covered in this training include many different implementations of eBPF, XDP, Ftrace, Kprobe, Uprobe, Netfilter, Systemtap, PAM, SSHD, HTTPD/Nginx, LD_PRELOAD-based code samples, and PoCs. Detection and forensics layers include LKRG, bpftool, Velociraptor IR, OSQuery, CLI-based /proc/ and /sys/ analysis, memory forensics with Volatility 2/3 Framework with the semi-automated RAM acquisition, Sysmon4Linux, Falco, Tracee, Sysdig, Tetragon, Sandfly Security, Zeek IDS, Suricata IDS, Moloch/Arkime FPC, Yara rules and more.
The hands-on content has been divided into user-space and kernel-space sub-sections. When you are done, dig deeper and create your own custom attack paths, then improve your detection coverage. Purple teaming for life!
If you want to enhance your understanding of Linux x86/x64 internals and stay prepared for Linux threats, this course is a must have!
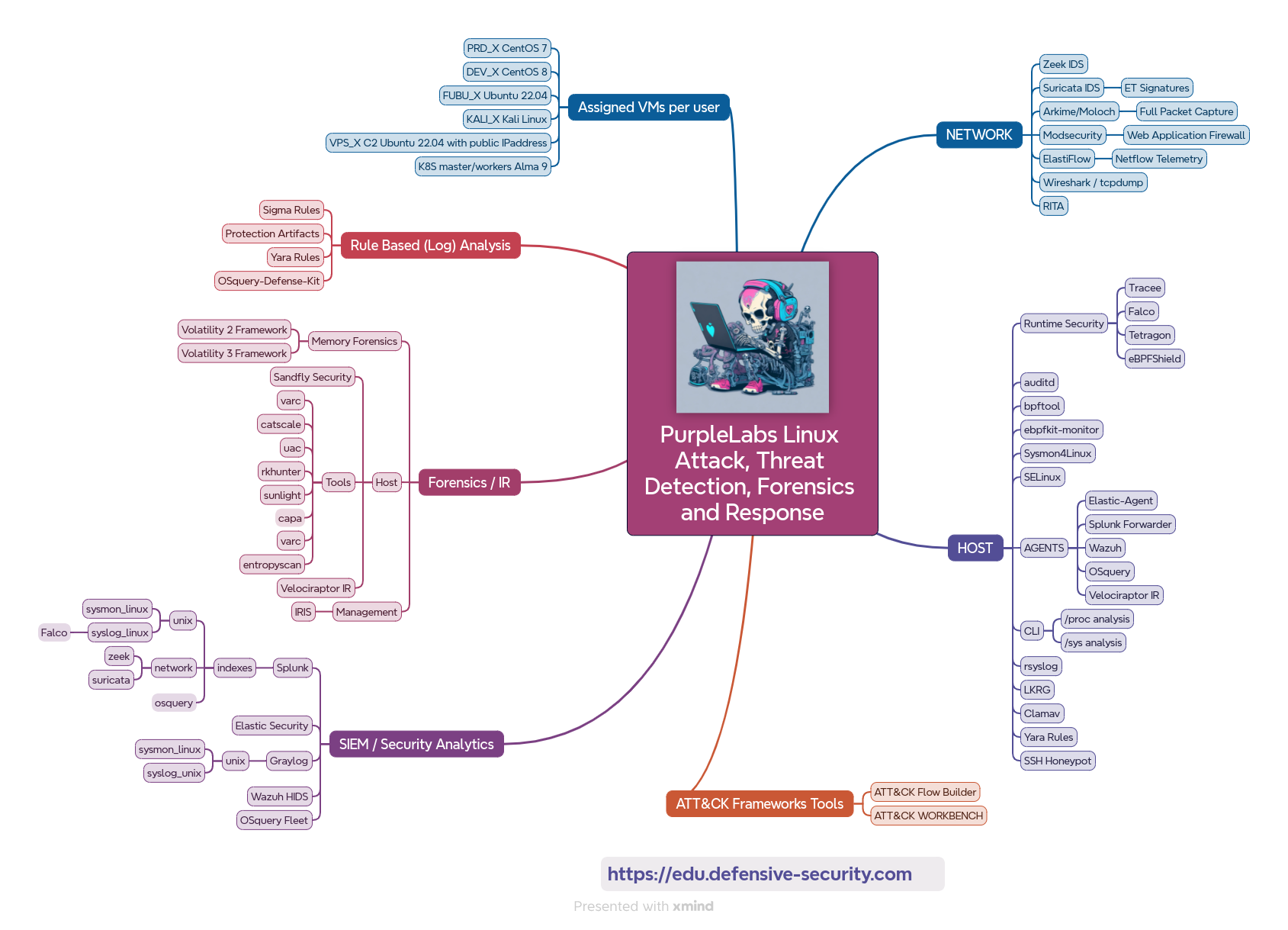
Through the hands-on labs, you will gain a perfect understanding of important DFIR Linux/Network internals and investigation steps needed to get the full picture of Linux attack paths including post-exploitation activities and artifacts left behind.
Dive into the world of Linux syscall hooking techniques, see hands-on how rootkits work in well-prepared Detection PurpleLabs Cyber Range, analyze and modify the source codes, find interesting behavior patterns in binaries and logs, learn what telemetry is needed to catch modern Linux threat actors, and find how to proactively validate and improve detection coverage with step-by-step Linux adversary emulations.
The idea around PurpleFlows Rapid Track is to quickly illustrate the lab features, Linux threat landscape, and possible detection/forensics methods using PurpleLabs components. Not everyone has the time and willingness to go through all the material and here my role is to provide you with a list of the most important and best-built scenarios. Remember to check the single lab as completed when it is done.
This module is dedicated to the introduction to the PurpleLabs environment, network setup and assigned virtual machines, available tools, hunting components, datasets, and telemetry. Use this short and easy section to better use the PurpleLabs platform and hands-on materials.
This section is about dynamic memory acquisition and live memory forensics of Linux boxes. Improve your memory forensics skills by playing with Volatility Framework 2/3 against a huge set of Linux attack use cases. The idea is simple. You make an offensive operation and in the next step, you download the RAM image and use Volatility Framework to find artifacts. The entire process has been automated, which allows you to focus on the merits. Memory forensics is also a cool approach for baselining low levels of your OS and apps!
A section about different kinds of network tunneling and pivoting techniques. Thanks to PurpleLabs you can easily jump through different subnets and hosts using protocols of your choice, then analyze your network flows and prepare IoC in IRIS.
Get to know the newest Linux attack paths and hiding techniques vs proactive detection
Learn current trends, techniques, and offensive tools for Discovery, C2, Lateral Movement, Persistence, Evasion, Exfiltration, Execution, Credential Access against Linux machines ← Linux Matrix ATT&Ck Framework
Learn ways to improve detection and sharpen your event correlation skills across many different Linux/network data sources
Get to know visibility/detection methods and capabilities of well-recognized Hunting and Detection tools, including Elastic Security, Velociraptor, Falco, Tracee, Tetragon, Kunai, Splunk, Moloch/Arkime, Zeek, Suricata, OSquery, Wazuh, Graylog, Sandfly
Find the malicious Linux activities and identify threat details on the network
Prepare your SOC team for fast filtering out Linux network noise and allow for better incident response handling
Find out how Detection / DFIR Open Source Software can support your SOC infrastructure
Understand the values of proactive Linux forensics scans vs manual and automated approaches to simulate attackers and generate anomalies
Identify Linux blind spots in your network security posture
Understand the value of the purple teaming approach, where you hunt for yourself and teammates

This package doesn't include VPN Access. You can purchase it separately.
Of course. After the purchase please send me an email with the details for issuing the invoice:
Company name
name/surname
address/country
VAT ID (if applicable)
The payment document/invoice from Podia/Stripe/Paypal is not a valid accounting document.
We issue the correct document upon request.
After the payment, you will get instant and lifelong access to online materials, of course, in the fully guided step-by-step format. Updates included!
No, it was not a priority, only hands-on lab experience.
The hands-on lab instructions and the PurpleLabs Cyber Range environment have been designed so that you can easily handle all instructions yourself.
You have to purchase a dedicated VPN access separately. We provide VPN for 30 and 90 days.
Definitely YES! I understand we are all busy, and I am flexible here - if someone wants to purchase the VPN Access hands-on in one week, month, or even 3 or 6 months after the course purchase - that’s fine :) Just ping me when you are ready to start the VPN PurpleLabs.